Application Gateway
Overview
Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that enables you to manage traffic to your web applications.
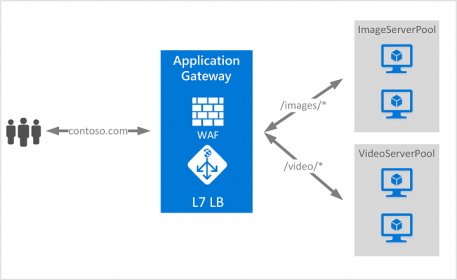
Traditional load balancers operate at the transport layer (OSI layer 4 - TCP and UDP) and route traffic based on source IP address and port, to a destination IP address and port. But with the Application Gateway you can be even more specific. For example, you can route traffic based on the incoming URL. So if /images is in the incoming URL, you can route traffic to a specific set of servers (known as a pool) configured for images. If /video is in the URL, that traffic is routed to another pool optimized for videos.
This type of routing is known as application layer (OSI layer 7) load balancing. Azure Application Gateway can do URL-based routing and more.
Features
The following features are included with Azure Application Gateway:
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) termination
Application gateway supports SSL termination at the gateway, after which traffic typically flows unencrypted to the backend servers. This feature allows web servers to be unburdened from costly encryption and decryption overhead. However, sometimes unencrypted communication to the servers is not an acceptable option. This could be due to security requirements, compliance requirements, or the application may only accept a secure connection. For such applications, application gateway supports end to end SSL encryption.
Web application firewall
Web application firewall (WAF) is a feature of Application Gateway that provides centralized protection of your web applications from common exploits and vulnerabilities. WAF is based on rules from the OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) core rule sets 3.0 or 2.2.9.
Web applications are increasingly targets of malicious attacks that exploit common known vulnerabilities. Common among these exploits are SQL injection attacks, cross site scripting attacks to name a few. Preventing such attacks in application code can be challenging and may require rigorous maintenance, patching and monitoring at many layers of the application topology. A centralized web application firewall helps make security management much simpler and gives better assurance to application administrators against threats or intrusions. A WAF solution can also react to a security threat faster by patching a known vulnerability at a central location versus securing each of individual web applications. Existing application gateways can be converted to a web application firewall enabled application gateway easily.
Multiple-site hosting
Multiple-site hosting enables you to configure more than one web site on the same application gateway instance. This feature allows you to configure a more efficient topology for your deployments by adding up to 20 web sites to one application gateway. Each web site can be directed to its own pool. For example, application gateway can serve traffic for contoso.com and fabrikam.com from two server pools called ContosoServerPool and FabrikamServerPool.
Requests for http://contoso.com are routed to ContosoServerPool, and http://fabrikam.com are routed to FabrikamServerPool.
Similarly, two subdomains of the same parent domain can be hosted on the same application gateway deployment. Examples of using subdomains could include http://blog.contoso.com and http://app.contoso.com hosted on a single application gateway deployment.
Redirection
A common scenario for many web applications is to support automatic HTTP to HTTPS redirection to ensure all communication between an application and its users occurs over an encrypted path.
In the past, you may have used techniques such as creating a dedicated pool whose sole purpose is to redirect requests it receives on HTTP to HTTPS. Application gateway supports the ability to redirect traffic on the Application Gateway. This simplifies application configuration, optimizes the resource usage, and supports new redirection scenarios, including global and path-based redirection. Application Gateway redirection support is not limited to HTTP to HTTPS redirection alone. This is a generic redirection mechanism, so you can redirect from and to any port you define using rules. It also supports redirection to an external site as well.
Application Gateway redirection support offers the following capabilities:
- Global redirection from one port to another port on the Gateway. This enables HTTP to HTTPS redirection on a site.
- Path-based redirection. This type of redirection enables HTTP to HTTPS redirection only on a specific site area, for example a shopping cart area denoted by
/cart/*. - Redirect to an external site.
Session affinity
The cookie-based session affinity feature is useful when you want to keep a user session on the same server. By using gateway-managed cookies, the Application Gateway can direct subsequent traffic from a user session to the same server for processing. This is important in cases where session state is saved locally on the server for a user session.
Websocket and HTTP/2 traffic
Application Gateway provides native support for the WebSocket and HTTP/2 protocols. There's no user-configurable setting to selectively enable or disable WebSocket support. HTTP/2 support can be enabled using Azure PowerShell.
The WebSocket and HTTP/2 protocols enable full duplex communication between a server and a client over a long running TCP connection. This allows for a more interactive communication between the web server and the client, which can be bidirectional without the need for polling as required in HTTP-based implementations. These protocols have low overhead, unlike HTTP, and can reuse the same TCP connection for multiple request/responses resulting in a more efficient utilization of resources. These protocols are designed to work over traditional HTTP ports of 80 and 443.